Data-based decisions – “Let the data speak”
The applications of data science are diverse and range from the calculation of key performance indicators (KPIs) to the creation of dashboards and complex machine learning approaches. The goal is always the same: Converting data into knowledge. However, before the analysis can begin, data must first be collected, processed, and stored.
Systematically record and process data
Unorganized raw data is of limited use without targeted processing. Companies generate a wide range of data, including transaction data, customer messages, inventory data, machine performance data, and reference data. However, these valuable data resources are often inadequately managed and not used efficiently. For profitable processing, data must be carefully reviewed, processed, validated, adjusted, and corrected. Although data preparation is a tedious task, it is an indispensable basis for all analyses and the resulting conclusions. Master data maintenance and data cleansing should therefore have a high priority in every company.
Company-wide governance is essential when using data science. The key figures in decision-relevant dashboards must be quality-assured and documented so that users can rely on the information provided.
Our Data Science Unit offers professional support in the identification and preparation of data requirements, especially for the development of dashboards in the areas of pricing and sales. We also assist in the development of comprehensive governance for data and KPIs. This enables your company to effectively utilize the full potential of existing data assets.
Different methods - always tailored to our customers
There are various options for analyzing data, depending on the target project. We tailor the choice of analysis tools to the customer and the project. Simple ad-hoc analyses do not always have to meet the high requirements of business dashboards. Often, a pragmatic approach using Excel and heterogeneous, incomplete data can quickly lead to sufficiently meaningful results. More advanced analyses need high-performance technology, such as artificial intelligence, to process large volumes of data or to recognize complex patterns.
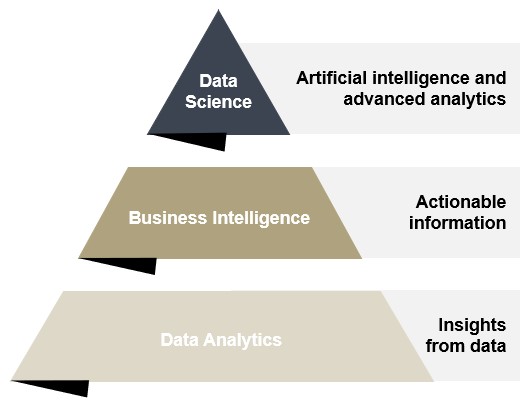
Data analytics: Individual analyses & tools
In the course of a pricing or sales project, questions often arise that can only be answered by quantitative analyses. Low-code solutions such as Power BI or Excel are pragmatic analysis tools, especially for smaller data volumes and clearly defined problems. Further advantages of these solutions are their user-friendliness and widespread adoption in companies. This makes it possible to create customized tools such as target price calculators or profitability analyses that can be used by the customer team without extensive training.
Business intelligence solutions
Thanks to modern CRM, ERP and accounting systems, most organizations already have a large amount of machine-readable data. The challenge with Business Intelligence (BI) solutions is to convert this data into dashboards, to enable fast decision-making. In contrast to individual tools and ad-hoc analyses, the requirements for data quality are significantly higher here. It is also necessary to involve a larger number of stakeholders in the development process. The creation of a business dashboard is therefore usually a comprehensive project that must take into account the interests and goals of its many users. However, the potential benefit of gaining a transparent, real-time insight into the company's current situation is a significant advantage that justifies the effort required.
Data science: Machine learning & artificial intelligence
Conventional analysis methods are often not sufficient to solve complex problems. In order to automatically identify clusters in extensive data sets, predict time series or assign categories, it makes sense to use machine learning. Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a key role in the creation of models for predictions ("predictive analytics") or in gaining new, in-depth insights through data mining. We use both traditional statistical methods and the latest machine learning techniques to master the diverse challenges faced by our clients.
Data science pays off
Data analysis enables companies to recognize new patterns and correlations. Through targeted evaluation, well-founded decisions can be made, processes optimized and future trends predicted, leading to increased efficiency and competitive advantages. The solutions that we develop together with our clients not only increase transparency about past developments, but also form the basis for their future corporate management.
1. Price waterfall analysis
Between the list price and the final invoiced net-net turnover of a company lies a multitude of price waterfall elements, which can either positively or negatively influence earnings. Many companies are keen to understand which factors have a significant impact on revenue and where untapped potential lies. A series of targeted analyses can be used to systematically identify weak points in pricing. These include the identification of price and volume effects, undifferentiated discounts or unfavorable freight and packaging costs. A deep understanding of the price waterfall and the associated price effects is one of the most effective tools for unlocking hidden potential. For many companies, this represents a decisive step towards significantly improved price management. With the help of the tools developed in the Data Science Unit, we identify the weak points in the price waterfall as part of a pricing audit.
2. Customer segmentation
The customer base is rarely homogeneous. The differentiation of customers into target groups is a prerequisite for the development and implementation of sales and marketing strategies. The aim here is to classify customers according to similar characteristics so that they can be addressed together. The size and number of segments depend on the industry, turnover, product portfolio and sales channel, among other factors. Cluster analyses can range from simple one-dimensional methods - such as differentiation according to purchase frequency - to multivariate methods such as conjoint analysis and factor analysis. We usually use data mining methods to determine customer or product clusters, which can also be applied to very large volumes of data.
3. Simulations of price and discount systems
The optimization of a price and condition system requires that the new rules can be evaluated with the help of a simulation. What will change if the new rules are introduced? For more complex systems, such a simulation is a prerequisite to correctly adjust the parameters of new pricing elements. It is always necessary to simulate changes at customer level in order to be able to implement the newly developed systems in the market. We have access to a range of reference applications to simulate price and discount systems. For special tasks, such as spare parts pricing, we have developed the software solution nueprice.
4. Prediction of price effects and tender-win probabilities
Modern machine learning methods make it possible to systematically gain insights into optimal pricing from companies' sales data. These methods can show which prices are reasonable and which volume changes can be expected when certain price levels are reached. This is particularly important for tenders. Here, these techniques can be used to determine at which price points there is an optimal trade-off between the profit margin and the probability of being awarded the contract. We develop models that can be used to quantify the factors influencing a customer’s willingness to pay. With the help of such models, it is possible to optimize prices and effectively support sales teams in their day-to-day business.
Utilize the potential of your data
A proven starting point for projects is the 360° data audit. In a three- to four-week check, we evaluate our client’s database and current analysis tools in order to identify any optimization potential and data science opportunities. The focus here is usually on data relating to the pricing of products and services but can also be extended to other areas on request.
As part of the data audit, we identify specific areas for action and draw up an implementation plan. This analysis gives the client a clear idea of which measures are particularly effective and necessary for them.
Prof. Roll & Pastuch – Management Consultants has many years of experience in the successful implementation of complex data science and analysis projects: We develop for you
- individually tailored pricing and sales tools
- established business intelligence solutions
- State-of-the-art artificial intelligence applications
This is how the transformation from big data to smart data succeeds.
Contact our data analytics & BI experts today
We are happy to answer your questions and provide further information.

Kai Pastuch
Kai Pastuch is Managing Director of Prof. Roll & Pastuch. Before joining as Managing Partner, he was Director at a leading international strategy and marketing consultancy. As a graduate in business informatics, he also manages our software company nueprice, which specializes in the pricing of spare parts with the product of the same name. Mr. Pastuch has extensive project management experience from numerous projects for large international companies and German medium-sized businesses in the areas of price management, marketing, sales and strategy. In addition to numerous publications in renowned journals and the publication of the reference books Praxishandbuch Preismanagement and Big Deal Management, he is a sought-after moderator and speaker on all aspects of sales and pricing. As a practice-oriented manager, he likes to get personally involved in our projects and contributes his broad experience in workshops and steerings.
